Design Technology

Design and Technology at CVPS
Design Technology LTP
Design Technology Progression of Skills
Curriculum Intent
What do we want to achieve with our DT curriculum?
At Clayton Village Primary School, it is our intent that children will learn to create, imagine and design products that solve real- life situations. We will give them the opportunity to explore relevant problems within a variety of contexts, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. This will then give children the opportunity to reflect and evaluate current products inspiring them to design and improve them independently. It is intended for children to acquire a broad range of subject knowledge and draw upon disciplines such as mathematics, science, engineering, computing and art. We believe that every child at CVPS deserves the opportunity to be practical, solve problems and gain skills for the future.
We want our children to:
We want our children to:
- Develop original ideas using their creativity and imagination.
- Be an informed consumer by considering the value, quality and craftsmanship of products.
- Draw on their knowledge of science, mathematics, ICT, engineering and art to inform their designs.
- Assess risk and be able to keep themselves safe.
- Be resourceful, innovative and enterprising.
- Talk about the impact of DT on daily life and the wider world (past and present).
- Be inspired to become the inventors and creators of the future.
- Have skills for life; cooking, sewing, woodwork and engineering.
Key features of our Design and Technology curriculum:
Design- Children use a design model to note their ideas and begin to develop an understanding of how their product will look as a result of their ideas. Providing children with the time to look at existing products and planning their own design based on their research. Giving children access to the products in real life so that they can use their senses as well as researching online and in books.
Make– Trial and error is a huge element of Design and Technology and enables children to build resilience and focus on the process as much as the outcome. Children will select a range of equipment and materials in order to create their product.
Evaluate – Children can then reflect on their own work and decide what has worked well and what could be improved. This involves looking at the product as a whole and including the positives and negatives of their product and comparing it to products that have already been produced.
Technical Knowledge – Building and using mechanisms and structures. Understanding and applying how electrical, mechanical and computing systems can work in their products.
Cooking and nutrition –
Early Years Foundation Stage
Pupils explore and use a variety of media and materials through a combination of child initiated and adult directed activities. They have opportunities to learn how to:
- Improving fine motor/scissor skills with a variety of materials.
- Joining materials in a variety of ways (temporary and permanent).
- Joining different materials together.
- Describing their junk model, and how they intend to put it together.
- Making a boat that floats and is waterproof, considering material choices.
Evaluate
- Giving a verbal evaluation of their own and others’ junk models with adult
support.
- Checking to see if their model matches their plan.
- Considering what they would do differently if they were to do it again.
- Describing their favourite and least favourite part of their model.
- Making predictions about, and evaluating different materials to see if they are
waterproof.
- Making predictions about, and evaluating existing boats to see which floats best.
- Testing their design and reflecting on what could have been done differently.
- Investigating how the shapes and structure of a boat affect the way it moves.
Technical Knowledge
- To know there are a range to different materials that can be used to make a model and that they are all slightly different.
- Making simple suggestions to fix their junk model.
Key Stage 1
Pupils are taught:
Design
- design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria
- generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mock-ups and, where appropriate, information and communication technology
Make
- select from and use a range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing]
- select from and use a wide range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their characteristics
Evaluate
- explore and evaluate a range of existing products
- evaluate their ideas and products against design criteria
Technical Knowledge
- build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable
- explore and use mechanisms [for example, levers, sliders, wheels and axles], in their products.
Key Stage 2
Pupils are taught:
Design
- use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at particular individuals or groups
- generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross-sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer-aided design
Make
- select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately
- select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities
Evaluate
- investigate and analyse a range of existing products
- evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work
- understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world Technical knowledge apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures understand and use mechanical systems in their products [for example, gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages]
- understand and use electrical systems in their products [for example, series circuits incorporating switches, bulbs, buzzers and motors] apply their understanding of computing to program, monitor and control their products.
Technical Knowledge
- apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures
- understand and use mechanical systems in their products [for example, gears, pulleys, cams, levers and linkages]
- understand and use electrical systems in their products [for example, series circuits incorporating switches, bulbs, buzzers and motors]
- apply their understanding of computing to program, monitor and control their products.
Cooking and Nutrition
Key Stage 1
- use the basic principles of a healthy and varied diet to prepare dishes
- understand where food comes from
Key Stage 2
- understand and apply the principles of a healthy and varied diet
- prepare and cook a variety of predominantly savoury dishes using a range of cooking techniques
- understand seasonality, and know where and how a variety of ingredients are grown, reared, caught and processed
Curriculum Implementation
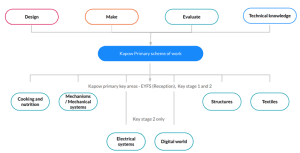
At CVPS, we give our children every opportunity to develop and secure their understanding of design and technology. We follow the 4 step design process: design, make, evaluate and use technical knowledge to create products for a real life purpose. With support from the subject leader, teachers offer a curriculum which covers structures, cooking and nutrition, textiles, mechanisms, electrical systems and the digital world over each term from Reception to year 6.
Children are taught the skills in line with the National Curriculum in Design Technology. Early in their education journey with us, in Reception we teach the children skills for life such as gluing, cutting, sewing, chopping and mixing in every year group and the children learn how to use tools safely.
At CVPS, we encourage children to look at existing products to gauge an idea of products that are already available and how they work. This then leads children to base their ideas on what they have seen but use their imagination to change the product by adding their own ideas.
How will this be achieved?
Clayton Village Primary School’s Design and Technology is supported by the KAPOW scheme to support staff with implementing the curriculum. Projects are planned purposefully so that children have the opportunity to revisit prior knowledge and build upon this. We use a progression of skills document to ensure that activities are planned so that pupils’ knowledge, understanding and skills are steadily developed as they move throughout school. At CVPS we follow the four stages of the cycle of research, design, make and evaluate, with each stage rooted with technical knowledge.
In order to promote creative teaching and the children’s enjoyment and curiosity for learning, Design and Technology is taught through a child led approach where appropriate.
Unit Structure & Lesson Structure
Over the Key Stage phase, each year group will cover three units of Design and Technology. In REC and KS1 children have the opportunity to revisit skills during ‘discovery time’
Curriculum Impact
The impact of children’s learning in Design Technology is an ongoing monitoring of children’s understanding, knowledge and skills by the class teacher, throughout lessons. This assessment is then used to inform differentiation, support and challenge required by the children. Design Technology is also monitored by the subject leader throughout the year in the form of book monitoring, looking at outcomes and pupil interviews to discuss their learning and understanding and establish the impact of the teaching taking place.
We want our pupils to grow into confident, independent learners, who aim high, value the creative process and are curious about the world around them.
At Clayton Village Primary School, we gather evidence from a variety of sources to assess the success of our Design and Technology curriculum. These include:
- Foundation Stage children are assessed within Expressive Arts and Design. Age related expectation levels are reported to parents at the end of the reception year.
- Class photo books to evidence pupils’ achievements
- Monitoring of planning
- Learning Walks – made by teachers to different classes
- Lesson Observations
- Scrutiny of Work – undertaken by teachers and Governors
- Self/peer-evaluation and critical discussion
- Talking to pupils about what they know
Our Aims at CVPS
Our Design and Technology curriculum embodies our school’s aims, so that children will leave our school with:
- A desire to aim high
- A respect for their peers, different cultures and the wider world around them
- Having experienced positive, happy memories
- A set of developed skills in research, design, make and evaluation
- An appreciation and understanding of the work of a range of artists, craftspeople and designers
- An inquisitive nature
- The ability to use materials to express themselves, their thoughts, feelings and ideas
- The ability to produce high-quality pieces of work in a variety of media that they can be proud of
- The ability to analyse and evaluate their work and the work of their peers, in a constructive way which leads to positive development within their practice
- The ability to then improve their work upon evaluation
Substantive Knowledge
Concepts and subject knowledge:
Substantive knowledge is the subject-specific content of design and technology which is taught through research and practice. This is the core subject knowledge, skills and vocabulary used about the designing and making processes and the contribution of designers from a range of genres, times and cultural traditions. We explore these through the lenses of substantive concepts which are taught through explicit vocabulary instruction as well as through the direct content and context of the study.
The substantive concepts that we develop through our Design and Technology curriculum are:
- Food and Nutrition
- Mechanisms
- Structures
- Electrical Systems
- Textile
Disciplinary Knowledge:
In addition to the core knowledge required to be successful within each of these elements, our curriculum outlines key aspects of how we intend to develop working as a designer. We organise our curriculum so that it focuses on developing different aspects of these competencies at different points. The features of working as a designer in our Design and Technology Curriculum are:
- Design – The art or process of deciding how something will look or work.
- Make – Create something by combining materials or putting parts together.
- Evaluate – Form an opinion of the value or quality of something after careful thought.
- Technical Knowledge – Building and using mechanisms and structures. Understanding and applying how electrical, mechanical and computing systems can work in their products.
Developing vocabulary: our aim is to ensure that our children are familiar with frequently occurring words that appear in various contexts and topics (including terms and concepts).
| DT Vocabulary progression document | |||||
| Vocabulary: Textiles | |||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| Pattern, join, mark out,
decorate, running stitch, needle, fabric. |
Template, quality, suitable, features, dye, overstitch, design, fray, mock-up, seam. | Fastening, compartment, zip, finishing technique, function, prototype, back stitch, felted, woven, knitted, bonded. | Aesthetics, seam allowance, pinning, embroidery,
back/blanket/cross stitch. |
Specification, tacking,
working drawing, clasp, pinking shears, design criteria, hem, reinforce, stem stitch, satin stitch, tie dye. |
Applique, annotate, evaluate, innovation, functionality, renewable, authentic, chain stitch. |
| Vocabulary: Electrical systems | |||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| User, fault, toggle switch, insulator, conductor, battery holder, crocodile clip | Series circuit, connection, push-to-make switch, push to-break switch, innovative, appealing, control box, input device, output device,
system |
Parallel circuit, light emitting diode, monitor, flowchart, design specification, reed switch, tilt switch | Light dependent resistor, interface control, micro
switch, latching switch |
||
| Vocabulary: Mechanisms | |||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| Wheels & Axles:
Wheel, axel, fixed, free, design, make, cutting, joining, hacksaw, vice, dowel, body, cab, shaping |
Slider & Leavers:
Mechanism, lever, slider, slot, pivot, guide/bridge, masking tape, fastener, pull/push, down, straight, work, design, evaluate, purpose |
Leavers & linkages:
Loose/fixed pivot, system, input, process |
Leavers & Linkages:
Loose pivot, fixed pivot, system, input, process, output, linear, rotary, reciprocating, innovative, appealing, linkage, oscillating |
Pulleys or Gears:
Pulley, gear, driver, follower, rotation, motor, belt, spindle, motor, circuit, switch, ratio, transmit, annotated drawings, exploded diagrams, functionality |
Pulleys or Gears:
Transmit, annotated drawings, exploded diagrams, functionality |
| Vocabulary: Structures | |||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| Freestanding Structures: Cut, fold, join, fix, weak, strong | Freestanding Structures: Structure, base, underneath, thicker, thinner, corner, point,
straight, curved, rectangle, cube, cuboid, cylinder |
Shell Structures:
Shell, structure, net, marking out, material, joining, three dimensional, stiff |
Shell Structures:
Assemble, prism, vertex, breadth, capacity, scoring, adhesives, reduce, reuse, recycle, corrugating, ribbing, laminating |
Frame Structures:
Reinforce, triangulation, stability, temporary, permanent, prototype, innovation, functional, design brief |
|
| Vocabulary: Nutrition | |||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
| Preparing Fruit & Vegetables: Fruit, vegetables, soft, juicy, crunchy, sticky, smooth, sharp, crisp, sour hard, flesh, skin, seed pip, core, slicing, peeling, cutting, squeezing, healthy diet, choosing, ingredients, planning, tasting, arranging | Healthy & Varied Diet: Texture, taste, appearance, preference, greasy, moist, fresh, savoury, hygienic, edible, grown, reared, caught, frozen, tinned, processed, seasonal, harvested | Celebrating Culture & Seasonality: Ingredients, yeast, dough, wholemeal, unleavened, baking soda, spice, herbs, carbohydrate, sugar, fat, protein, vitamins, nutrients, gluten, | |||
| allergy, intolerance, savoury, seasonality, pour, mix, knead, whisk, beat, combine, fold, rubbing in |
Key Symbols